Java 集合之 Map
2020/2/12
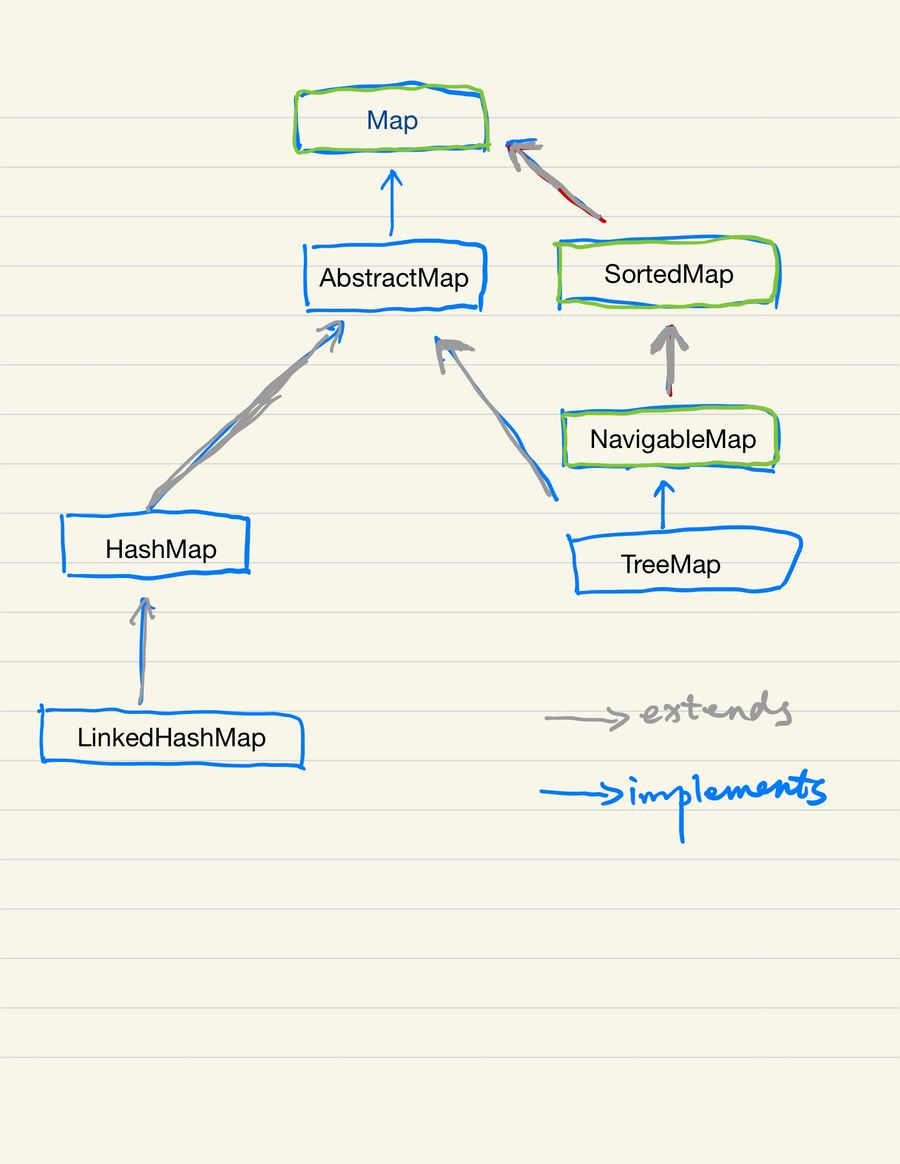
Java 中的 Map 实际上并不属于 Java Collection,因为他并没有继承自 Collection 接口。 在 Java 中,Map 是一个接口
An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value.
AbstractMap 实现 Map 接口,是 Java 中所有 Map 实现的基类。
This class provides a skeletal implementation of the {@code Map} interface, to minimize the effort required to implement this interface.
Java 中常用的 Map 有 HashMap, LinkedHashMap, TreeMap, 这个和 Set 类似。
HashMap
Hash table based implementation of the {@code Map} interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits {@code null} values and the {@code null} key. (The {@code HashMap} class is roughly equivalent to {@code Hashtable}, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time.
在源码的开头注释就写了 HashMap 和 Hashtable 的区别,
- 非线程安全的
- key 和 value 都允许是 Null
HashMap 是以 key 的哈希值作为key的值来存储的,他能提供 O(N) 级别的访问效率。 看一下源码,put 的大致思路是:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 如果 table 没有初始化,那就初始化一下
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 计算index,并对 null 做处理
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 节点存在
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 节点是树节点
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 节点是链表
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
这个代码,功能复杂,大致步骤是这样:
- 检查是否需要初始化和是否需要扩容
- 计算下标 (n-1) & hash, 如果不存在,则直接赋值
- 如果存在,获取已存在的值,并且考虑是链表还是树,
- 如果是链表,检查下是否需要转换成红黑树结构
- 替换旧的值
- 检查是否需要扩容
其中还涉及到是否需要把链表结构变成树结构,在元素减少的时候,把树结构变成链表结构。
添加元素的时候,还考虑是否需要扩容,扩容的时候会对重新做 rehash, rehash 就会导致不稳定
LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 和 HashMap 的区别主要就是 Linked 这个字,他在内部维护一个双向链表的实现。并由这个双向链表来保持遍历顺序的稳定,通常来说这个顺序由插入时顺序决定。
LinkedHashMap 同样也是线程不安全的。
LinkedHashMap 提供一个特殊的构造函数,遍历顺序根据最后访问时间, accessOrder = true, 默认情况下 accessOrder = false, 遍历时根据插入顺序
/**
* Constructs an empty {@code LinkedHashMap} instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - {@code true} for
* access-order, {@code false} for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
这种方式特别时候构建一个 LRU 缓存数据,
TreeMap
TreeMap 实现了 NavigableMap, 而 NavigableMap 继承了 SortedMap。 因此 TreeMap 中的元素都是按照他们的 Comparable 实现或者 Comparator 排序的,存储是有序的。因为实际是以 tree 的形式存储的,因此 add,remove 和 contains 都可以保证 log(n) 的时间复杂度。
A Red-Black tree based {@link NavigableMap} implementation. The map is sorted according to the {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of its keys, or by a {@link Comparator} provided at map creation time, depending on which constructor is used.
什么时候用哪个 Map 结构呢?
根据特性来决定使用哪个结构
| 特性 | HashMap | LinkedHashMap | TreeMap |
|---|---|---|---|
| 遍历 | 无序 | 根据插入顺序或者最后访问时间 | 根据 Comparable 结果 |
| 线程安全 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
所以,总的来说,HashMap 符合通用的场景; 如果你需要一个保持插入时顺序的,或者要构建一个 LRU 缓存,用 LinkedHashMap。 如果你想要一个能排序的,比如根据姓名能依次输出结果的Map,那么就使用 TreeMap